What Is Backend Development Explained
What Is Backend Development Explained
Backend development is the work that happens behind the scenes of any application. It’s all about the server, the application's logic, and the database.
Think of it like the engine room of a ship. While users are up on the polished deck (the frontend), the backend is where all the power, machinery, and critical operations are chugging away to make the ship actually move.
Deconstructing Backend Development

Imagine you’re using your mobile banking app. You tap a button to check your account balance. That single tap triggers a request from your phone (the client, or frontend) to a powerful, remote computer (the server).
The backend code running on that server immediately springs into action. It verifies your identity, securely finds and pulls your account information from a database, and then sends that data whizzing back to your phone. A moment later, it appears neatly on your screen.
This entire invisible process is the very heart of backend development. It's the foundational layer that handles data, security, and the core business rules that make an application actually do something. Without a solid backend, even the most beautiful user interface is just an empty, non-functional shell.
To get a clearer picture, it helps to see how the two sides compare.
Backend vs Frontend At a Glance
This table breaks down the core differences between the engine room and the user-facing deck.
| Aspect | Backend Development (The Engine Room) | Frontend Development (The User Interface) |
|---|---|---|
| Main Focus | Server-side logic, databases, APIs, security, and performance. The 'how it works'. | User-facing elements, visual design, interactivity, and user experience. The 'what you see'. |
| Core Technologies | Python, Node.js, Ruby, Java, PHP; SQL & NoSQL databases (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB). | HTML, CSS, JavaScript; Frameworks like Angular, Vue.js, and for mobile, Flutter. |
| Key Responsibilities | Building and maintaining server infrastructure, managing databases, creating APIs, handling user authentication. | Designing and building the user interface, ensuring responsiveness, and implementing client-side logic. |
| Where it Runs | On the server, completely invisible to the end-user. | In the user's browser or on their mobile device. |
Ultimately, frontend and backend are two sides of the same coin, working in tandem to create a seamless experience for the user.
The Role of the Backend
The backend is responsible for a huge range of critical tasks that users never see but absolutely rely on. Its primary functions boil down to a few key areas:
- Data Management: Securely storing, retrieving, updating, and deleting information from a database.
- User Authentication: Handling user logins, managing permissions, and making sure only the right people can access specific data.
- Business Logic: Executing the core rules and processes that define how the application works, like calculating a shopping basket total or processing a payment.
- Server Communication: Managing all incoming requests from the frontend and sending back the right data or responses.
It's no surprise that skilled professionals who can build and maintain these systems are in incredibly high demand. In fact, software developers have recently re-entered the UK’s top five most in-demand jobs.
Sectors like FinTech and healthcare are built on complex and secure backends, driving a huge need for experts. This is why backend developers in the UK often command salaries around £50,000 per year, reflecting just how vital their role is. You can explore more data on the UK software development market to see how this trend is growing.
In short, if the frontend is what you see, the backend is how it all works. It's the hidden logic and infrastructure that powers every single interaction, from posting a photo on Instagram to booking a flight online.
Why It Matters for App Performance
A robust backend is non-negotiable, especially for mobile applications, including those built with high-performance frameworks like Flutter.
Flutter is brilliant at creating slick, responsive user interfaces that feel great to use. But it's the backend that has to deliver the data, process transactions, and keep information synchronised across all of a user's devices.
A slow or poorly built backend will directly lead to a sluggish, frustrating user experience—no matter how gorgeous the frontend looks.
The Three Pillars of Backend Architecture
To really get to grips with what is backend development, we need to look past the analogies and break down the core components that make it tick. Every functional backend, whether it's for a simple mobile app or a sprawling enterprise system, rests on three fundamental pillars: the server, the database, and the application logic. These three work in a constant, coordinated dance to process requests and deliver information.
Let's stick with a simpler analogy: a restaurant. When a customer places an order (that's a user request), it kicks off a chain of events in the kitchen.
The kitchen itself is the server – the central hub where everything happens. The restaurant’s organised pantry is the database, holding all the ingredients (data). And the head chef? That’s the application logic, directing exactly how to combine those ingredients to create the final dish.
This simple hierarchy shows how the server fields requests, the application logic processes them based on a set of rules, and the database stores all the necessary data.
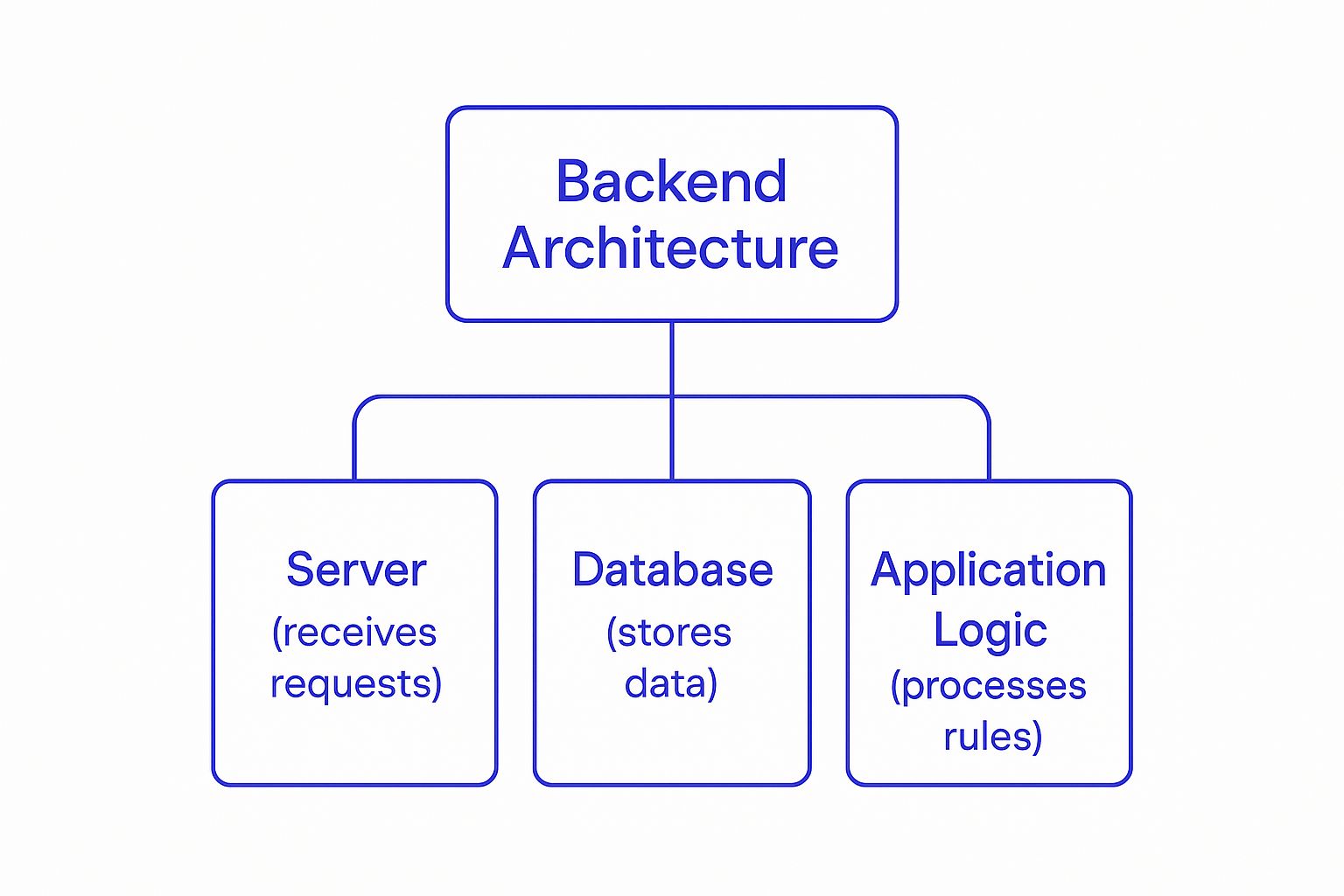
This gives you a great visual of the distinct but deeply interconnected roles each pillar plays. Now, let’s unpack each one.
The Server: The Digital Kitchen
The server is the first point of contact for any request coming in from the frontend. Think of it as a powerful computer (or, more likely, a network of them) that’s always on, listening for requests sent over the internet. When you tap a button in an app, you're essentially sending a message straight to this server.
Its main job is to accept these requests, figure out what's being asked, and then pass them along to the right part of the backend to be handled. In our restaurant, the server is the kitchen’s order window. It takes the order from the waiter (the API) and makes sure it gets to the right station to be prepared. Servers can be physical machines tucked away in a data centre or virtual instances running in the cloud on platforms like AWS or Google Cloud.
The Database: The Organised Pantry
Once a server gets a request, it almost always needs information to fulfil it. That’s where the database comes into play. A database is a highly structured system designed for storing, managing, and retrieving huge amounts of data efficiently and securely. It’s the digital version of that meticulously organised pantry, where every single ingredient has its proper place.
Databases generally come in two main flavours:
- SQL (Relational) Databases: These are like spreadsheets on steroids, with very strict rules. Data is organised into tables with predefined relationships, making them perfect for structured information like user profiles or transaction histories. Common examples include MySQL and PostgreSQL.
- NoSQL (Non-Relational) Databases: These are far more flexible, like a collection of documents in a filing cabinet. They’re brilliant for unstructured or semi-structured data, like social media posts or real-time gaming data. MongoDB is a huge player in this space.
Choosing the right database structure is absolutely critical for performance and scalability down the line. To get a better sense of how these systems are designed, you can learn more about entity relationship diagrams in our essential guide to database blueprints. Understanding this "blueprint" is key to building a data storage system that won't fall over when things get busy.
The Application Logic: The Head Chef
The final, and arguably most important, pillar is the application logic (often called business logic). This is the code that acts as the "brain" of the backend. It's the set of rules and procedures that dictates how data is created, changed, and sent back to the user.
If the server is the kitchen and the database is the pantry, then the application logic is the head chef. The chef takes the order, knows which ingredients to pull from the pantry, and follows a specific recipe to prepare the perfect dish before sending it back out.
This logic is what makes an app do what it’s supposed to do. For an e-commerce app, the application logic is what calculates your shopping basket total, applies a discount code, and processes your payment. For a social media app, it’s the algorithm that decides which posts to show you in your feed.
Written in languages like Python, Node.js, or Dart, this code is what turns raw data into a meaningful, interactive experience for the user. Together, these three pillars form the powerful, invisible engine that drives every modern application we use.
Choosing Your Tools: Backend Languages and Frameworks

Just like a master chef has a specific knife for every task, a backend developer needs the right programming languages and frameworks to build a solid, efficient system. A big part of understanding what is backend development is getting to know the tools of the trade. The technology stack you pick will directly impact how quickly you can build, how well your app scales, and the kinds of features you can roll out.
This isn’t about finding one “best” language. It’s about choosing the perfect tool for the job. The needs of a high-frequency trading platform in London's FinTech scene are worlds apart from a real-time chat app for a startup. Each language brings its own strengths, community support, and ecosystem to the table.
Popular Backend Programming Languages
A programming language gives you the basic commands to tell a server what to do. In the UK tech scene, a few key players have become dominant, each carving out its own niche. Let's take a look.
- Python: Famous for its clean, readable syntax, Python has become a giant in data science, machine learning, and FinTech. Its simplicity means you can develop ideas fast, making it a favourite for startups that need to build and iterate quickly.
- Node.js (JavaScript): Traditionally a frontend language, JavaScript now runs on the server thanks to Node.js. It’s brilliant for building fast, scalable network applications, especially services needing real-time communication like chat apps or live sports updates. Its non-blocking I/O model is a game-changer for handling lots of connections at once.
- Java: A true veteran of the backend world, Java is known for its stability, security, and "write once, run anywhere" philosophy. It’s still the backbone of huge enterprise systems, banking applications, and complex e-commerce platforms where reliability is non-negotiable.
- PHP: As one of the original languages of the web, PHP still powers a huge chunk of the internet—including platforms like WordPress. It's often praised for being straightforward and having massive amounts of documentation and community support, which makes it a really accessible choice for web development.
The choice of language is a strategic one. It influences hiring, development speed, and long-term maintenance. For instance, London's thriving FinTech industry often leans on Python for its powerful data analysis libraries, while a startup focused on a social media app might prefer Node.js for its real-time capabilities.
Understanding Frameworks: The Developer's Toolkit
If a language provides the raw ingredients, a framework is the pre-built kitchen station—complete with an oven, hobs, and organised prep surfaces. Frameworks are bundles of pre-written code, libraries, and tools that give developers a structured foundation to build on.
They handle all the common, repetitive stuff like routing requests, managing database interactions, and beefing up security. This frees up developers to focus on what makes the application unique.
Put simply, using a framework drastically speeds up development time and helps enforce best practices, which leads to more reliable and maintainable code. You’re not reinventing the wheel every time you start a new project. For our clients, this means a faster route to market and a more dependable final product.
Popular Backend Technologies and Their Use Cases
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a quick breakdown of some popular frameworks and the languages they’re built on. Each one is designed to solve specific problems efficiently.
| Technology | Primary Use Case | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Django (Python) | Rapid development of secure and maintainable web applications. | Includes a powerful Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) for easy database interaction and a built-in admin panel. |
| Express.js (Node.js) | Building fast and minimalist web applications and APIs. | Highly flexible and unopinionated, giving developers complete control over the application's structure. |
| Spring (Java) | Developing high-performance, enterprise-grade applications. | Comprehensive ecosystem that covers everything from security to data access and microservices. |
| Laravel (PHP) | Creating modern web applications with elegant and expressive syntax. | Offers a rich set of features like a built-in templating engine and tools for tasks like authentication and caching. |
Ultimately, picking the right combination of language and framework is a critical step in the backend development process. It sets the stage for everything that comes next.
How APIs Bridge the Frontend and Backend

So, we have the user-facing frontend and the powerful backend engine. How do they actually communicate? They can’t just shout at each other across the digital divide. They need a translator, a messenger, and a set of strict rules to govern their interactions. This crucial go-between is the Application Programming Interface, or API.
Think back to our restaurant analogy. You (the frontend) don't just march into the kitchen (the backend) to demand your meal. Instead, you give your order to a waiter—the API—who acts as the perfect intermediary.
The waiter knows the menu, understands the kitchen's lingo, and makes sure your order is passed on correctly. Once the dish is ready, they bring it back to your table. The API does exactly this, allowing the frontend and backend to talk to each other without needing to know the messy, complicated details of how the other side works.
The API as a Contract
At its heart, an API is a formal contract between two pieces of software. It spells out the specific requests one application can make to another and defines the exact format of the replies it will get back. This "contract" is what makes their conversation predictable and reliable.
For instance, a weather app's API might say: "If you send me a city name in this specific format, I promise to send you back the current temperature, humidity, and forecast in that exact format."
This structured approach is what allows completely separate systems, even those owned by different companies, to work together so well. It’s how your favourite travel app can pull flight data from an airline's servers or how a payment button on a website can securely talk to a bank.
An API establishes a clear set of rules for interaction. It's the universal language that lets the frontend confidently ask for what it needs, knowing the backend will understand and respond in a predictable way.
Building these robust communication channels is a massive part of what backend development is all about.
Introducing REST APIs
When it comes to building APIs for web and mobile apps, one style has become the undisputed industry standard: REST (Representational State Transfer). A RESTful API uses the same web protocols your browser uses to load websites—specifically HTTP—to get the job done.
REST APIs are incredibly popular because they are simple, scalable, and stateless. "Stateless" is a key concept here. It means every request from the frontend contains all the information the backend needs to process it. The server doesn't have to remember anything about previous requests, which makes the whole system much easier to manage as more users come on board.
This approach revolves around a few core ideas:
- HTTP Methods: It uses standard commands like
GETto retrieve data,POSTto create something new,PUTto update it, andDELETEto get rid of it. - Endpoints: These are just specific URLs where the API can be accessed, like
/users/123to get information about a particular user. - Standard Data Formats: Data is usually exchanged in a human-readable format, most commonly JSON (JavaScript Object Notation).
Building a solid API is a critical skill in backend development. To dig deeper into how these connections work, you can learn more by reading our guide on what API integration is and why it's so vital for modern apps. For a Flutter app, a well-designed REST API is the lifeline that delivers all the dynamic content and functionality to the user's device.
Powering High-Performance Flutter Apps with a Strong Backend
A stunning mobile app is only half the story. For UK developers using Flutter, a robust backend isn't just a nice-to-have—it’s the engine that creates world-class experiences that keep users coming back. While Flutter is brilliant at crafting beautiful and fluid user interfaces, the backend does all the heavy lifting behind the scenes.
This server-side powerhouse is what securely authenticates users, stores critical data, sends out push notifications, and runs the complex business logic that makes your app valuable. It's the silent partner that turns the frontend's promises into reality.
The Symbiotic Relationship Between Flutter and the Backend
Think of your Flutter app like a high-performance electric car. The design is sleek, the interior is intuitive, and the acceleration is instant. That’s the user experience Flutter delivers. But that car is completely useless without its sophisticated battery and power management system—the backend—to supply the energy and control its core functions.
Recent benchmarks consistently show Flutter’s top-tier performance for building natively compiled applications from a single codebase. It’s a framework built for speed and responsiveness. But to really unlock its full potential, it needs to be paired with an equally capable and scalable backend. A weak backend will throttle even the most optimised Flutter UI, leading to slow load times, laggy interactions, and a frustrating experience for your users.
What’s the backend’s role here? It’s to make sure that when a user taps a button in your Flutter app, the data they need is delivered instantly and reliably. The backend is the source of truth and power that gives the frontend’s performance real meaning.
A strong backend supports a Flutter application by providing several critical services that are simply impossible to handle on the user's device alone.
Essential Backend Functions for a Modern Flutter App
To go beyond a simple, static display, a Flutter app needs a backend to manage its dynamic and interactive features. These are the core jobs the server-side architecture handles.
- User Authentication and Management: Securely handling sign-ups, logins, and profile management is a fundamental backend task. It makes sure user data is protected and that access is properly controlled.
- Database Management: From user-generated content to product inventories, the backend is responsible for storing, retrieving, and managing all of the application's data in a structured and efficient way.
- Push Notifications: Sending timely and relevant alerts to users—like order updates or new messages—is a powerful engagement tool managed entirely by the backend, which talks to services like Firebase Cloud Messaging or Apple Push Notification Service.
- Business Logic Execution: Any complex calculation, data processing, or rule-based action (like processing a payment or applying a discount) is executed on the server to ensure consistency and security.
- Third-Party API Integrations: When your app needs to connect with other services, like a payment gateway or a mapping service, the backend handles these integrations, keeping sensitive keys and logic secure.
Choosing the Right Backend Technology for Flutter
One of the best things about working with Flutter is its versatility. Because the frontend and backend communicate via APIs, you're free to choose pretty much any backend technology that fits your project's needs. That said, some choices offer a more streamlined development experience.
Firebase, a Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) platform from Google, is a hugely popular choice for Flutter developers. It provides a suite of ready-made backend services, including authentication, real-time databases (Firestore), and cloud functions, which can massively speed up development.
For more custom solutions, developers often build their own backends using various languages and frameworks. Interestingly, Dart—the same language used to build Flutter apps—can also be used on the server with frameworks like Dart Frog. This allows for a single, unified language across the entire stack, which can really simplify the development process for your team. Alternatively, you can explore how to create a cloud application with Flutter and Google Cloud Platform for a powerful, scalable infrastructure.
Ultimately, the choice of backend technology comes down to your app's specific requirements, scalability needs, and your team's expertise. But one thing is certain: a high-performance Flutter app is only as strong as the backend that powers it.
Building Your Career as a UK Backend Developer
So, you're looking to break into backend development? It’s a fantastic career choice, especially within the UK's buzzing tech scene. But moving from knowing what backend development is to landing a professional role takes more than just textbook knowledge. It’s a mix of the right technical skills, some hands-on experience, and a real feel for what the industry wants.
Let's walk through a clear roadmap to get you there.
The absolute bedrock of any backend developer's career is their technical toolkit. From London's high-stakes FinTech firms to Manchester's fast-moving e-commerce players, employers expect you to have a solid command of the core technologies. Getting these under your belt is your first, most important step.
Essential Technical Skills for the UK Market
If you want to be a competitive candidate, your portfolio needs to scream "I can build and maintain the engine of an application." While every company has its preferred tech stack, a strong foundation in these areas is completely non-negotiable.
- Programming Languages: You need deep, practical knowledge of at least one major backend language. Think Python, Node.js, or Java.
- Database Management: Data is everything. You have to be comfortable with both SQL databases like PostgreSQL and NoSQL ones like MongoDB to handle it all properly.
- API Design: Can you build a solid RESTful API? This is the bridge to the frontend, so being able to design, build, and look after these is a must.
- Cloud Platforms: Most modern applications live on the cloud. Experience with services like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure is hugely in demand.
- Version Control: You'll be working in a team. That means Git isn't optional; it's a fundamental requirement for collaboration.
Beyond Code: Soft Skills That Matter
Here's a secret that many junior developers miss: your technical skills will only get you so far. UK employers are looking for people who can work well with others and genuinely contribute to the company's bigger picture. These soft skills are often what separates a decent developer from a truly great one.
Problem-solving is right at the top of that list. A backend developer's job is, at its core, to untangle complex logical puzzles. You need to show you can approach challenges methodically. On top of that, clear communication and a collaborative spirit are vital. You'll be constantly talking to frontend developers, project managers, and other stakeholders to get a project over the line.
Your Career Path and Salary Expectations
The career ladder for a backend developer in the UK is pretty well-defined. You'll typically start as a junior, move to a mid-level role, and then progress to a senior or lead developer. Once you have some solid experience, you can branch out into specialisms like DevOps, cloud architecture, or data engineering.
Now, let's talk money. Salaries are shaped by your location, your experience, and any specialist skills you bring to the table. Unsurprisingly, London-based jobs pay more to offset the higher cost of living. A UK developer's salary can start from around £30,000 for entry-level positions and climb to over £100,000 for senior roles, with backend specialists often sitting comfortably at the higher end of that scale.
For comparison, cities like Glasgow and Leeds see average salaries around £38,049 and £33,813, respectively. If you have in-demand skills in areas like cloud computing or machine learning, you can expect that to give your earning potential a significant boost. It's worth checking out more detailed reports to understand the key factors influencing software developer salaries in the UK.
Your career path is a continuous journey of learning and adaptation. By building a strong technical foundation and honing your soft skills, you position yourself for long-term success in the dynamic UK tech industry.
Common Backend Development Questions
As you get your head around backend development, a few questions always seem to pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to give you a clearer picture of where the backend fits into the grand scheme of things.
Is Backend Harder Than Frontend?
That’s the million-dollar question, isn't it? The honest answer is that it's a bit like asking if it's harder to be an architect or a structural engineer. They’re just different beasts, requiring different mindsets.
Frontend is all about what the user sees and interacts with—the visual design, the feel of the buttons, the flow of the user journey. It's a blend of creative flair and technical know-how.
The backend, on the other hand, is the hidden machinery. It’s about pure logic, data architecture, security, and performance. You're building the engine, not designing the car's interior. Some people find the abstract, complex problem-solving of the backend more of a challenge, while others are more wired for the creative-technical mix of the frontend. It really boils down to your own natural strengths and what you find most interesting.
Which Backend Technology Should I Learn First?
When you're just starting out, you want a language that's welcoming and has a strong community to back you up when you get stuck.
- Python with Django: Python is famous for its clean, readable syntax, which makes it a fantastic first language. When you pair it with a "batteries-included" framework like Django, you get a really clear structure for building a complete application right out of the box.
- JavaScript with Node.js and Express: If you've already dabbled in frontend development, you'll know JavaScript. Learning Node.js is a brilliant next step because it lets you use the exact same language on the server. It just feels natural.
Both are brilliant choices, and you'll find plenty of job opportunities for them right here in the UK.
How Does Global Competition Affect UK Developers?
Make no mistake, the UK's tech scene doesn't exist in a bubble; it's part of a massive global ecosystem. The number of software developers worldwide is climbing fast, and some projections suggest India might soon have more developers than the US. You can get a sense of the scale by checking out these software developer population trends on OutsourceAccelerator.com.
This global talent pool has a direct impact here, influencing everything from salary expectations to the sheer level of competition for roles. For UK-based developers, this means standing still isn't an option. The key to staying competitive is to keep learning and specialising in high-demand areas like cloud infrastructure, data security, or specific DevOps practices.
Backend development isn't just a technical role; it's a critical business function that powers the digital economy. The high demand and competitive salaries reflect the immense value that skilled backend engineers bring to any organisation.
By constantly honing your skills, you can carve out a real career advantage and prove your value in a busy marketplace.
Ready to build a high-performance mobile app with a powerful backend? The expert team at App Developer UK specialises in creating stunning, natively compiled Flutter applications supported by robust and scalable server-side architecture. Let us bring your vision to life. Contact us today.